Difference between revisions of "Earth Observation Satellites"
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
Several relevant Figures of Merit exist for Earth Observation Satellites. | Several relevant Figures of Merit exist for Earth Observation Satellites. | ||
The imaging system in particular is constrained by four types of resolution: | The imaging system in particular is constrained by four types of resolution: | ||
''' | * '''Spatial [m]''' | ||
* Spectral [nm] | * Spectral [nm] | ||
* Temporal [days] (also called Return Time) | * Temporal [days] (also called Return Time) | ||
Revision as of 05:16, 1 October 2020
Technology Roadmap Sections and Deliverables
Roadmap Overview
Design Structure Matrix (DSM) Allocation
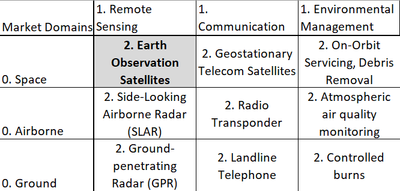
We have designated Earth Observation Satellites (2EOS) as a Level-2 Technology. It is present in the Level 1 Markets of 1) Low-Earth Orbital Technologies and Remote Sensing Technologies. For other examples of intersections on the basis of these markets, see the following figure:
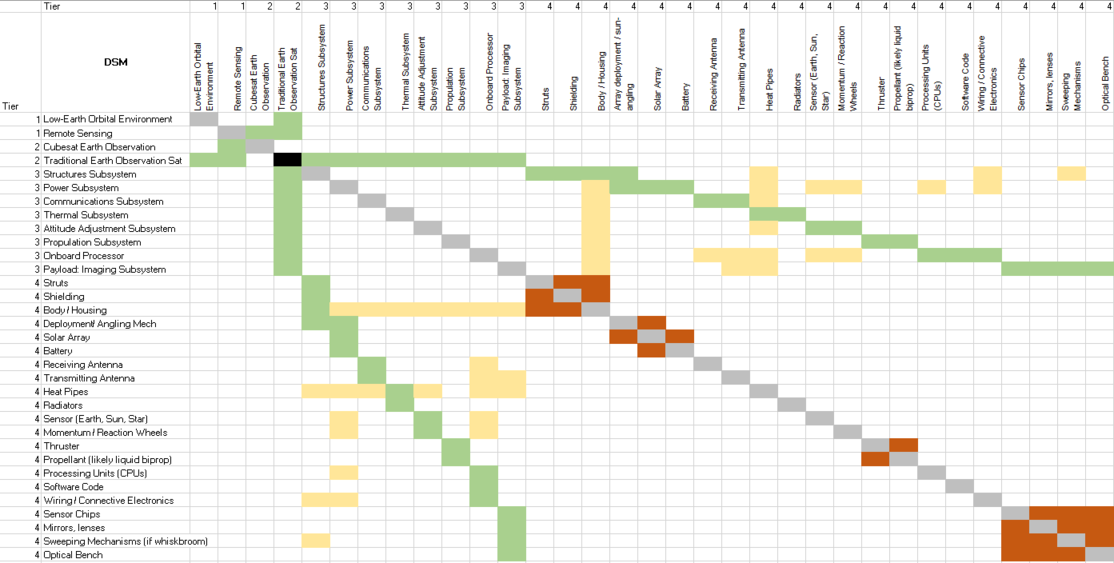
Our Design Structure Matrix (DSM) is as follows:
Legend: Green: Direct Component (solar arrays are a component of the Power Subsystem) Yellow: Cross-relationships between technologies and other subsystems (heat pipes interact with all other subsystems to transfer heat) Orange: Physical interactions between Level four technologies within the same subsystem (solar arrays interact with any deployment and angling mechanisms)
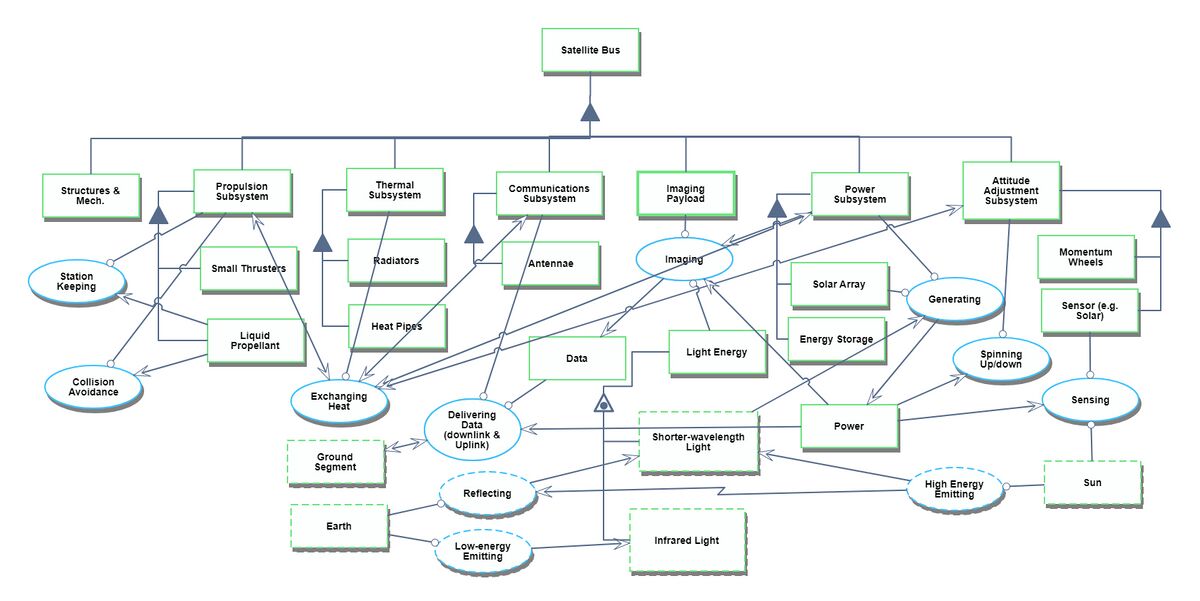
Roadmap Model using OPM
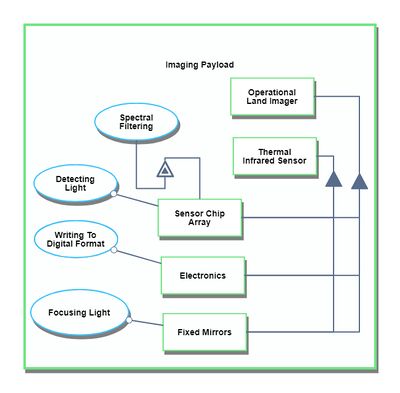
Our Object Process Diagram (OPD) is pictured below, complete with a Level Zoom to examine components of the Imaging Subsystem.
Figures of Merit (FOMs)
Several relevant Figures of Merit exist for Earth Observation Satellites. The imaging system in particular is constrained by four types of resolution:
- Spatial [m]
- Spectral [nm]
- Temporal [days] (also called Return Time)
- Radiometric [bits]
We will consider spatial resolution as principle among these, for most applications, including surveying, land management, urban planning, and disaster relief. Some hard tradeoffs exist between these. Generally, spatial resolution decreases with increasing spectral resolution. A minimum threshold of energy must reach the imaging sensor in order to resolve an image, and the smaller the band of electromagnetic radiation considered, the less energy received. Wider accepted bands (panchromatic) have more difficulty discerning color and material reflectivity, but gain in spatial resolution. Radiometric resolution is constrained primarily by cost and the available size for the imaging payload within the bus. The following figures show estimations of the improvement in spatial resolution over time.