Difference between revisions of "Wind Turbine - Energy Harvesting"
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
The table below is to show a list of FOMs of 2WTG. | The table below is to show a list of FOMs of 2WTG. | ||
[[File: | [[File:2WTGFOM2.png|center]] | ||
The unit cost, and capacity per wind turbine are both extremely important figures of merit. When looking into what wind turbine to buy, these would influence which brand and model should be purchased. While one wind turbine may be significantly cheaper than another, the capacity of a more expensive turbine might be much greater. It is also important to consider the | The unit cost, and capacity per wind turbine are both extremely important figures of merit. When looking into what wind turbine to buy, these would influence which brand and model should be purchased. While one wind turbine may be significantly cheaper than another, the capacity of a more expensive turbine might be much greater. It is also important to consider the availability of the turbine. This is essentially average hours of operation due to unfavorable wind conditions. There is a range of wind speeds any turbine can operate at, from the cut in wind speed at the lower end of the range, to the maximum safe operating speed at the high end. The region in which a wind turbine is assembled affects the availability of the turbine, but by expanding the operational wind speeds, the availability can be increased. | ||
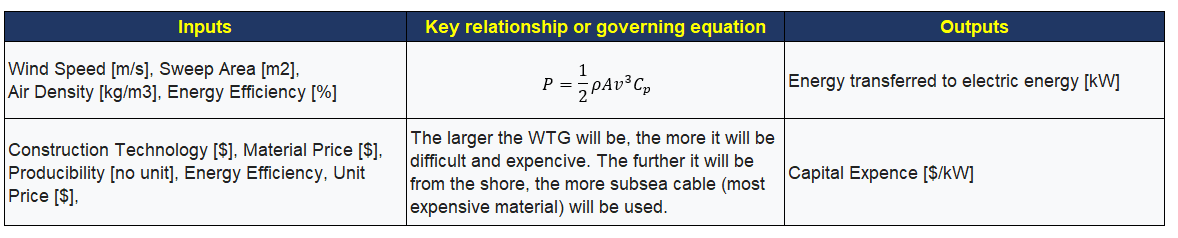
Furthermore, a couple of detail FOM with related formula and relationship is shown in the table below. | |||
[[File:2WTGFOM3.png|center]] | |||
==Alignment with Company Strategic Drivers== | ==Alignment with Company Strategic Drivers== | ||
Revision as of 02:21, 8 October 2019
Technology Roadmap Sections and Deliverables
Team 3 is to present a "level 2” roadmap of Wind Turbine Generators. The following code is the identifier.
- 2WTG - Wind Turbine Generator
Roadmap Overview
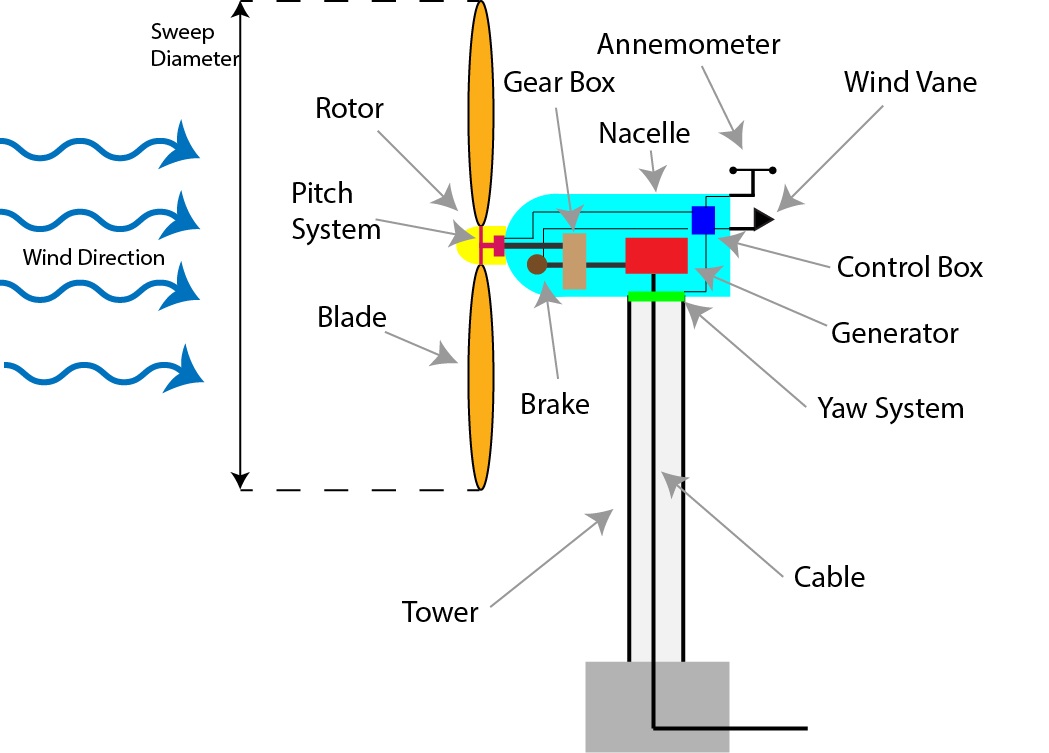
Wind turbines are used to harvest kinetic energy from the wind and transform that energy into electricity. A rotor, typically with three airfoil blades, rotates using the force of lift. A system of gears is used to transfer rotational energy of the hub to a high-speed shaft which feeds into a generator. The generator then utilizes the rotational energy to generate electricity and deliver it down the tower through a cable. An anemometer and weather vane are used to determine the wind speed and direction. The data that is collected is processed in the control box, which then adjusts the pitch of the blades and yaw of the nacelle for optimal operating conditions. Wind turbines can be assembled on land or water and usually generate energy proportional to their sweep area.
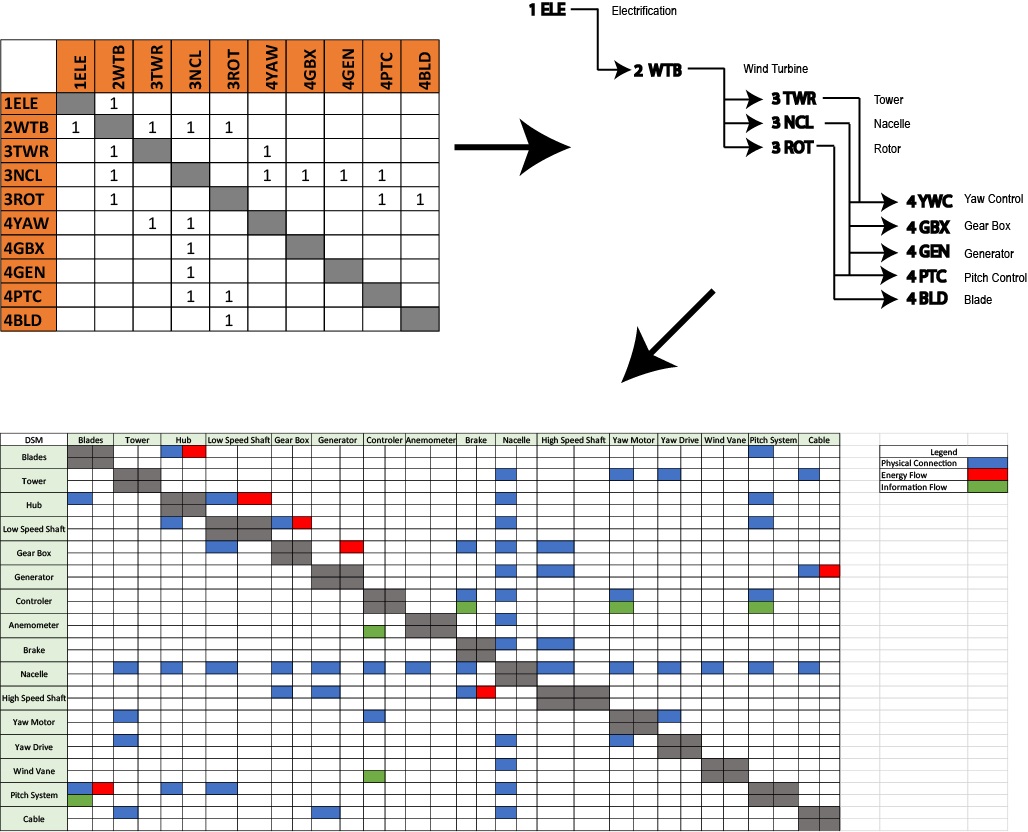
Design Structure Matrix (DSM) Allocation
The 2-WTB tree in the upper right corner displays some of the key components of a wind turbine (2WTB), that when individually improved, enhance the overall performance and figures of merit of the wind turbine. The wind turbine can be broken down into its three main portions: a tower (3TWR), a nacelle (3NCL) and a rotor (3ROT). The three main wind turbine parts stand on the shoulders of other technologies, which if removed or damaged, can significantly affect the wind turbine. The tree can then be expanded into a more complex matrix that shows how most of its components are interconnected. Many of the parts are connected physically, some transfer energy, and others share information. The tree also exposes the purpose of the wind turbine itself, which is to aid in overall electricity generation or electrification (1ELE). Wind turbines can be combined into wind farms which together can replace a carbon releasing power plant.
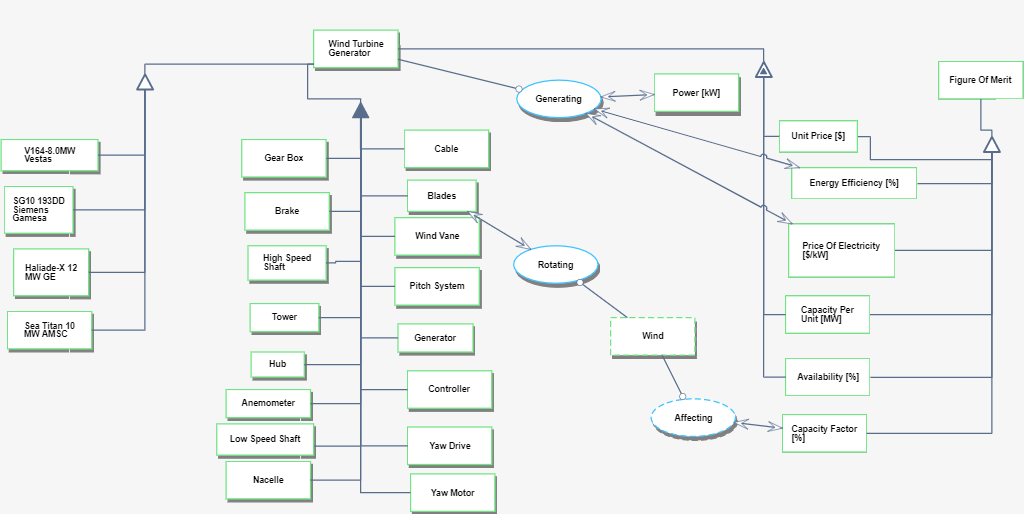
Roadmap Model using OPM
Team 3 hereby displays OPD of 2WTG - Wind Turbine Generator (WPG) This consists of level 2 decomposed WTG, associated products and figure of merit (FOM).
Associated OPL is displayed below. This represents the relationships among each object shown in the OPM above.
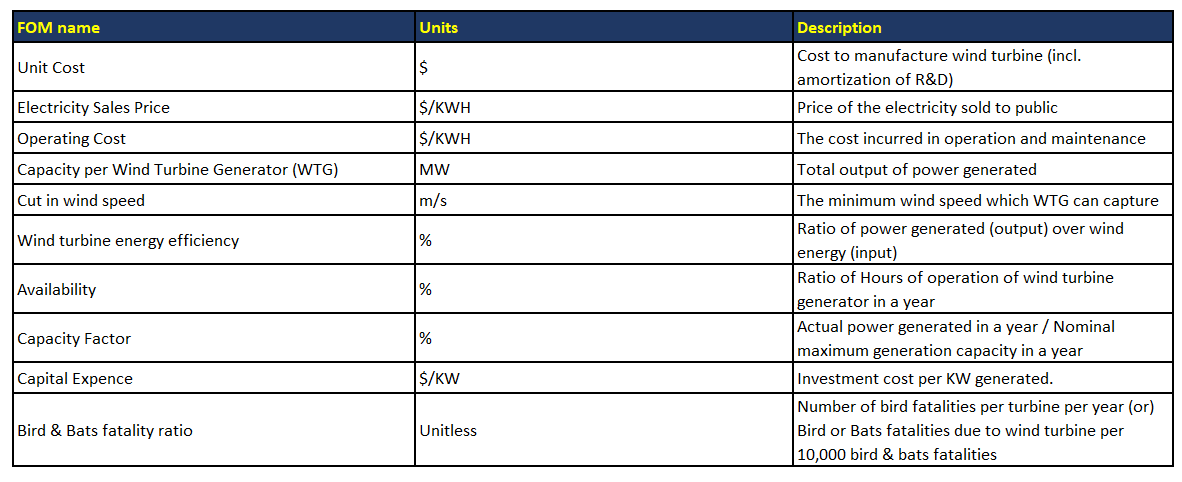
Figures of Merit
The table below is to show a list of FOMs of 2WTG.
The unit cost, and capacity per wind turbine are both extremely important figures of merit. When looking into what wind turbine to buy, these would influence which brand and model should be purchased. While one wind turbine may be significantly cheaper than another, the capacity of a more expensive turbine might be much greater. It is also important to consider the availability of the turbine. This is essentially average hours of operation due to unfavorable wind conditions. There is a range of wind speeds any turbine can operate at, from the cut in wind speed at the lower end of the range, to the maximum safe operating speed at the high end. The region in which a wind turbine is assembled affects the availability of the turbine, but by expanding the operational wind speeds, the availability can be increased.
Furthermore, a couple of detail FOM with related formula and relationship is shown in the table below.